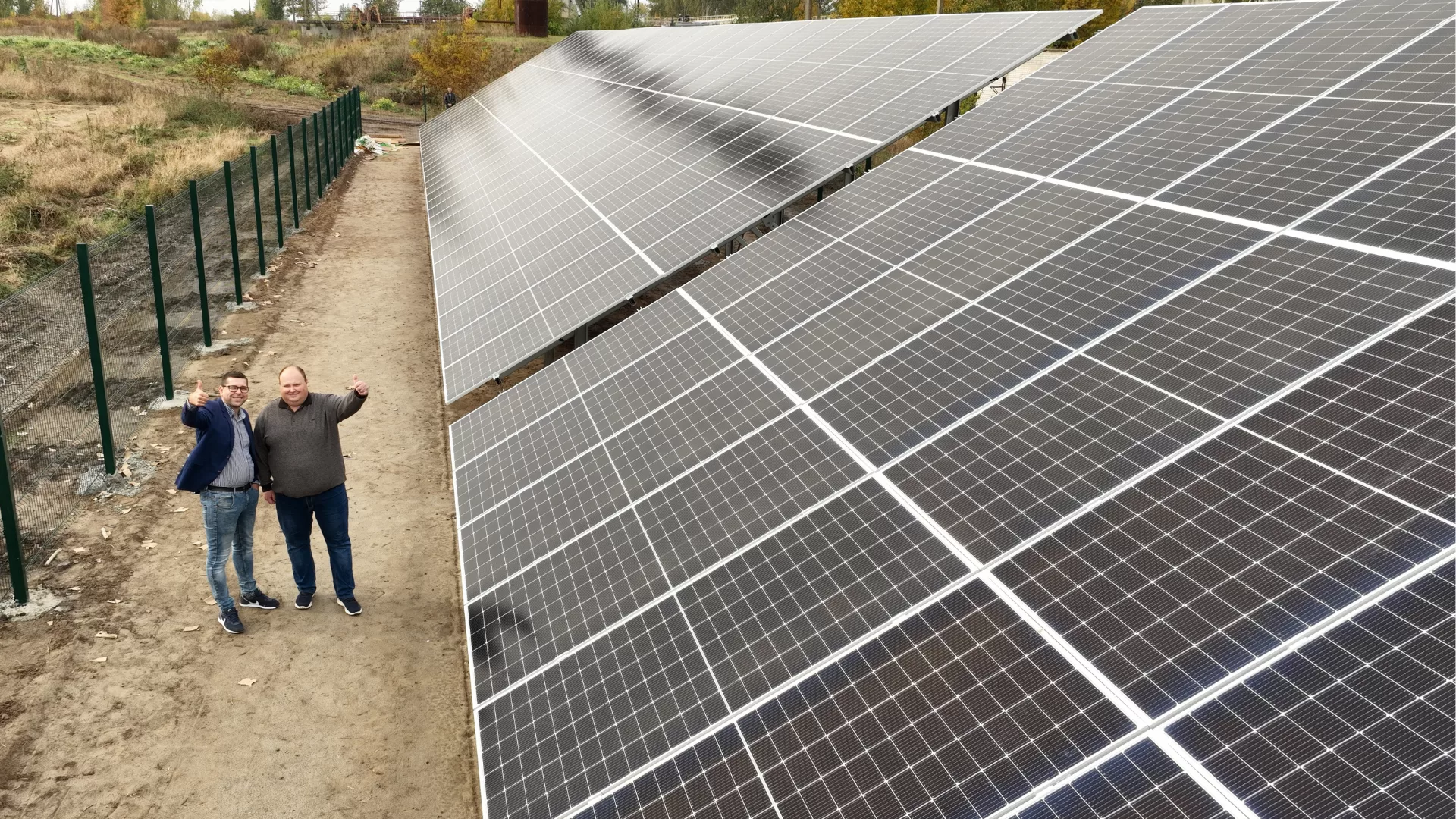
Over the three years of full-scale war, Ukraine has lost approximately 70% of its electricity generation capacity. Continuous Russian attacks on energy infrastructure and increased energy demand during the winter further exacerbate the challenges in the energy sector. In this context, ensuring a stable power supply to critical infrastructure has become a top priority.
The NGO Ecoclub advocates for the development of decentralized renewable energy as one of the solutions to this pressing issue. Specifically, installing solar power plants (SPPs) at critical infrastructure sites can significantly enhance the energy security of communities.
Since early 2022, Ecoclub, in collaboration with local communities, has installed more than 40 SPPs for critical infrastructure, including seven for water utilities. These solar plants not only help save public funds on electricity but also ensure uninterrupted operations during crises.
However, implementing these projects has revealed several challenges and barriers that could hinder the deployment of SPPs for water utilities. This article explores these obstacles and opportunities in detail and offers recommendations on how to overcome them.
Why SPPs Benefit Critical Infrastructure
1. Ensuring Energy Security and Stability
Decentralized SPPs generate electricity on-site, enabling critical infrastructure like water utilities to operate more reliably during blackouts and grid failures. SPPs can produce power even when the grid is down, ensuring continuous service delivery to residents.
For instance, during a blackout in Sumy, an SPP installed at the local water utility kept the facility running for two hours, allowing the reservoir to fill and supply water to city hospitals. This minimized the impact of power outages on water consumers. The plant’s solar panels have a capacity of 100.57 kW, supported by batteries with a total capacity of 81.6 kWh.
2. Saving Public Funds
Water utilities are among the largest electricity consumers in Ukraine, accounting for about 3% of the country’s total consumption. Installing SPPs can significantly reduce electricity costs, providing substantial financial relief to local budgets.
For example, an SPP at the water utility in Zviahel, funded by the local budget, saved approximately 900,000 UAH in six months. Before installation, the utility’s treatment facilities consumed 46-48% of its electricity; now, this figure has dropped to 36-37%. The savings can be redirected to other community needs, such as equipment upgrades or social programs.
3. Scaling Renewable Energy Projects
Successful SPP installations can encourage further renewable energy initiatives in the community. After completing one project, communities gain practical experience and confidence to pursue new ventures.
For instance, following the installation of an SPP at a hospital, the Zviahel community expanded their efforts, implementing additional solar projects for water utilities and other critical facilities.
4. Reducing Environmental Impact
Using renewable energy sources like solar power reduces greenhouse gas emissions and improves environmental conditions. During blackouts, most water utilities rely on diesel generators, which are costly and environmentally harmful.
A diesel generator operating four hours per blackout can produce 73,000 kWh annually, consuming about 18,250 liters of diesel. This results in annual expenses of €98,550 and nearly 49 tons of CO2 emissions. SPPs mitigate these impacts by reducing dependency on fossil fuels and improving air quality.
5. Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Installing SPPs often motivates enterprises to adopt other energy efficiency measures, such as modernizing pump systems or optimizing water supply and wastewater systems. This not only cuts energy costs but also improves service quality.
Explore the document Challenges and Opportunities for Solar Power Plants in water and wastewater sector in Ukraine
Challenges and Opportunities for Solar Power Plants in water and wastewater sector in Ukraine (1838 downloads )Barriers to SPP Deployment for Water Utilities
1. Dependence on Local Government Decisions
Most water utilities in Ukraine are municipal enterprises, meaning their operations heavily rely on local government decisions. Implementing SPP projects requires approvals from local councils, which can lead to delays and complications.
Challenges include obtaining land use permits, approving financial plans, and navigating political interests. Delays in decision-making can cause communities to miss out on grants or technical assistance.
2. Difficulty Securing Funding
Municipal enterprises often face financial constraints due to low service tariffs and high operational costs, which limit their creditworthiness and ability to attract investments. Limited internal funds, difficulties obtaining loans or grants, and reliance on state or donor support present significant hurdles.
Additionally, international loans often require repayment in foreign currencies, making enterprises vulnerable to exchange rate fluctuations. For instance, the depreciation of the hryvnia could increase loan servicing costs.
3. Land Allocation Challenges
Securing land for SPP installation involves a complex and bureaucratic process, including land management project development, council approvals, and adherence to Ukraine’s Land Code. These steps require specialists, incur costs, and can be influenced by political factors, leading to delays or additional expenses.
4. Complicated Permitting Processes
Current legislation lacks clear guidelines on permitting for rooftop SPPs, leading to legal uncertainties. This results in inconsistent interpretations by authorities, complicating project approval.
The permitting process involves obtaining initial design data, developing project documentation, undergoing expert review, securing construction permits, and commissioning the facility. These steps can delay projects, increase costs, and risk permit denials.
5. Lack of Effective Information Policies
Water utilities often lack sufficient information about opportunities to collaborate with international donors and NGOs. This results in missed chances to secure grants or technical assistance and limited awareness of available support programs.
6. Need for Skilled Personnel
Operating and maintaining SPPs requires specialized knowledge. Many enterprises lack such expertise, necessitating hiring additional staff or training existing personnel, which increases operational costs and risks improper SPP usage.
Overcoming Barriers
1. Streamlining Approval Processes
Government bodies should develop clear and transparent procedures for land allocation and permitting. Setting legally mandated timelines for reviewing applications and granting approvals can expedite the process.
2. Developing State Support Programs
Introducing state subsidies, grants, and preferential loans for enterprises installing SPPs can encourage investment in renewable energy. Tax incentives or exemptions would further promote such initiatives.
3. Legislative Reforms
Simplifying the permitting process, particularly for rooftop SPPs, and reducing documentation requirements could remove significant barriers.
4. Facilitating ESCO Contracts
Legal safeguards for funds and assets under ESCO contracts can foster trust and encourage enterprises to adopt these agreements, which fund energy efficiency projects through savings.
5. Raising Awareness and Providing Information Support
Conducting awareness campaigns, establishing support centers, and actively collaborating with NGOs like Ecoclub can enhance knowledge and engagement.
Funding Sources for SPPs
1. ESCO Contracts
Energy service companies fund and implement energy-saving measures, with payments made from cost savings, eliminating the need for upfront investments.
2. International Funding
Programs like U-LEAD, NEFCO, USAID’s Energy Security Project, and loans from EBRD and EIB offer financial support for renewable energy projects.
3. Ukrainian Bank Loans
Banks such as Ukrgazbank, Oschadbank, and Ukreximbank offer preferential loans for SPP projects.
Conclusion:
Installing SPPs at water utilities is a strategic step toward enhancing energy security, saving public funds, and reducing environmental impact. Addressing legislative gaps, developing support programs, and fostering collaboration with international organizations are crucial. By doing so, water utilities can lead the way in decentralized renewable energy adoption, ensuring reliable services for communities.
For consultation or further inquiries, contact us at office@ecoclubrivne.org.