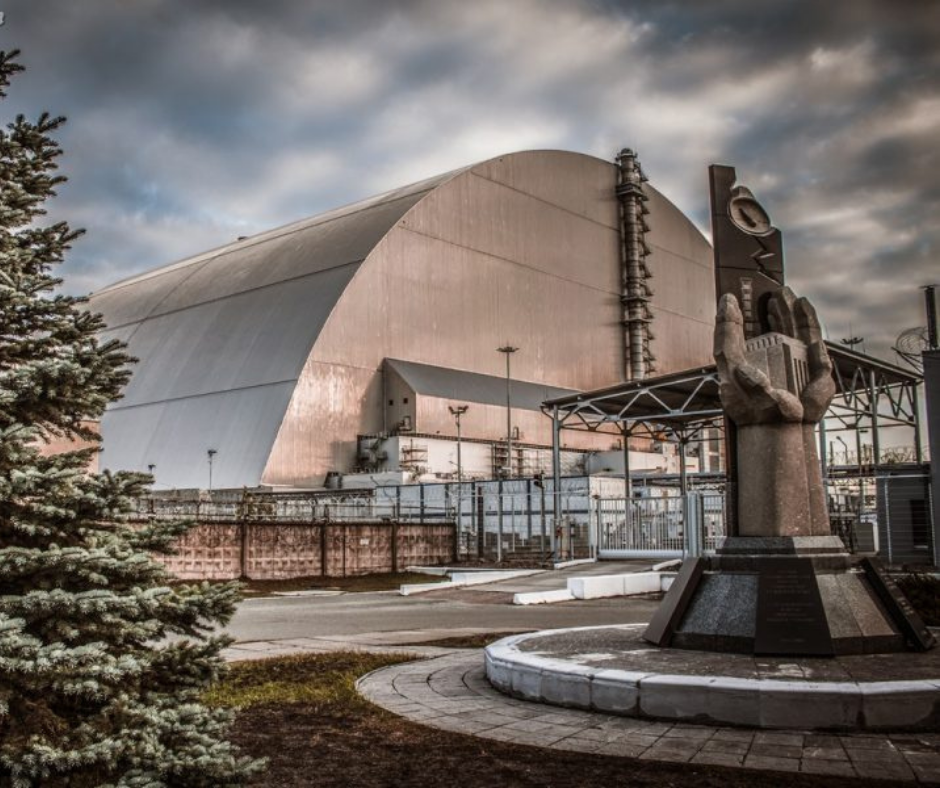
At the beginning of the full-scale invasion, Russia captured the Chornobyl nuclear power plant. National guard troops, that had protected the station were captured as well. Engineers and other technical staff were forced to work non-stop for more than 600 hours. As a result of shelling power outages occurred, which led to the de-electrization of all nuclear facilities, including The Storage of spent nuclear fuel. Ukraine was dangerously close to a new nuclear disaster.
We are going to talk about the seizure of ChNPP, the consequences of Russian nuclear terrorism, and who is in charge of nuclear security in Ukraine.
What was the danger?
On the 24th of February, prime-minister Denys Shmyhal informed, that Russian troops have captured ChNPP. Russians captured not only the nuclear facilities but also an entire Exclusion zone. On the 9th of May Energoatom informed, that ChNPP and its satellite-city Slavutych are de-electrizated.
Electricity is required to cool spent fuel storage facilities, which store about 20,000 spent fuel assemblies (a set of fuel elements used as fuel for nuclear power plants) from three Chernobyl reactors:
«They are stored in “pools” under a layer of water, as they emit heat for a long time after immersion. To remove residual heat and cool the assemblies, stable and continuous operation of water pumps that supply water and force it to circulate is required. If the pumps do not work, the temperature in the pool will rise, and the water will heat up and evaporate. As a result, it could lead to the destruction of assemblies and radiation leakage», said Olga Lyashchuk, Ecoclub project coordinator.
Because of power outages for a long time safety depended only on the work of diesel generators. Fuel for their normal functioning remained only for 48 hours.
Without the generators, critical temperature could be achieved in about seven days, said the Petro Kotin from Energoatom. As a result, there could be a danger of radiation leakage which can lead to acute lethal local exposure and to long-term lethal radiation doses within a radius of several kilometers from the accident site.

Even a small increase in water temperature (about 40°C) may cause malfunctions in the controlling and measuring system.
Therefore, the technical staff will face a problem with measuring the condition of The Spent nuclear fuel storage. The restoration of the power supply depended on the cessation of fighting in the Exclusion Zone, so Ukrenergo employees fixed the power line several times only after the shelling ended.
Another dangerous factor — is the continuous work of the employees (more than 600 hours). Office of the General attorney said, that Russian invaders forced personnel to work non-stop without the ability to move freely in the territory of ChNPP. They also were forbidden to get medical aid. Such pressure could lead to errors during the work.
«They wanted to run the facility. They wanted to get information about all the procedures, documents, and operations. I was scared. Interrogations were frequent, sometimes they were using force,» Oleksandr Lobada, head of the station’s radiation safety department.
Under pressure, staff understood the threat of a permanent power outage. This could lead to a loss of control over all automated security systems. Also, the fire extinguishing and ventilation system would not work, which could lead to an increase in the radiation dose received by the personnel.
«Additional problem was that Russians have captured a night shift of personnel. This is good, given that, compared to the day shift, the number of workers is smaller, and fewer people were in captivity. However, the workload on night shift workers increased, as they had to perform day shift work as well. The captured personnel were not physically able to carry out all the work in the required amount, mainly at the station itself. For example, they could not stabilize the Sarcophagus under the New Safe Configuration or visit spent nuclear fuel storage facilities,» said Olga Lyashchuk, Ecoclub project coordinator.
A partial rotation of personnel was possible only on the 26th day of the war. They were replaced by volunteer workers: The Energoatom boat delivered 49 workers and took 51 via the Pripyat River.
What is the current situation?
Russians abandoned captured territory on 31 March but had taken captured national guards. Currently, the station is operating normally: both the Shelter facility and the spent nuclear fuel storage facility, which were twice de-energized due to damage to power lines.
Chief of Energoatom Petro Kotin informed, that the critical infrastructure of Spent fuel storage has not been damaged.
Instead invaders looted and destroyed the Central Analytical Laboratory in Chernobyl, which cost 6 million euros. This was announced on March 22 by the State Agency of Ukraine for Exclusion Zone Management. The laboratory conducted research on samples of radioactive waste from the Chornobyl Exclusion Zone for physical, chemical and radiation indicators:
«The laboratory contained highly active samples and samples of radionuclides, which are now in the hands of the enemy, with which, we hope, he will harm himself and not the civilized world,» said the press secretary of the Agency.

According to Oleksandr Syrota, Chairman of the Public Council at the State Agency for Exclusion Zone Management, Russian invaders also destroyed a historical ChNPP archive, some documents were thrown away like trash.
Direct connection of ChNPP with IAEA was resumed on 20th April. International experts plans to visit Chornobyl nuclear power plant in late April, on the anniversary of the 1986 tragedy, to «assess nuclear safety and radiological protection, deliver important equipment and repair remote monitoring systems.»
Who is in charge of nuclear security?
IAEA establishes standards of nuclear safety and provides technical support for member states. The Agency consists of 164 member countries. The IAEA is part of the system of international organizations of the United Nations, with which it has an agreement since 1959.
On March 9, Ukraine informed the IAEA about the problems with the power supply on the Spent fuel storage. Instead, the agency said in a statement that it did not see a critical impact on security after all facilities of ChNPP were cut off: «IAEA Director General Rafael Grossi has said that this event violates a key security principle in ensuring uninterrupted energy supply, but in this case the IAEA does not consider the situation critical,» the IAEA’s official Twitter page said.
Where to check the radiation level?
Information on radiation levels can be found on Saveecobot. It is an online system that also provides information on air pollution levels, including harmful substances. Information on the radiation level in the Rivne region is published by the Rivne Regional Center for Hydrometeorology on the official Facebook page.